2021. 5. 11. 17:39ㆍData science/Python
HTML for Web Scraping
*Web Pages have lots of variable information.
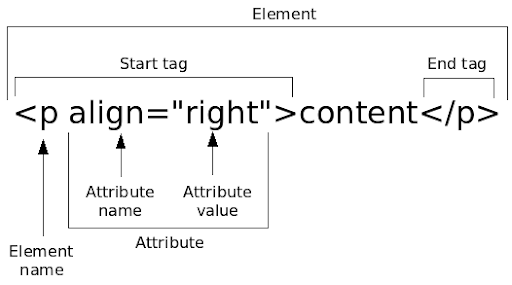
*HTML Tags : marked with blue ink inside of angle brackets
*HTML Composition : head, body, <p> tag : paragraph
*HTML Anchor Tag - a piece of text which marks the beginning and/or the end of a hypertext link.
: <a hef ="https://www.ibm.com"> IBM webpage </a>
*HTML Hyperlink tag - link to the web page
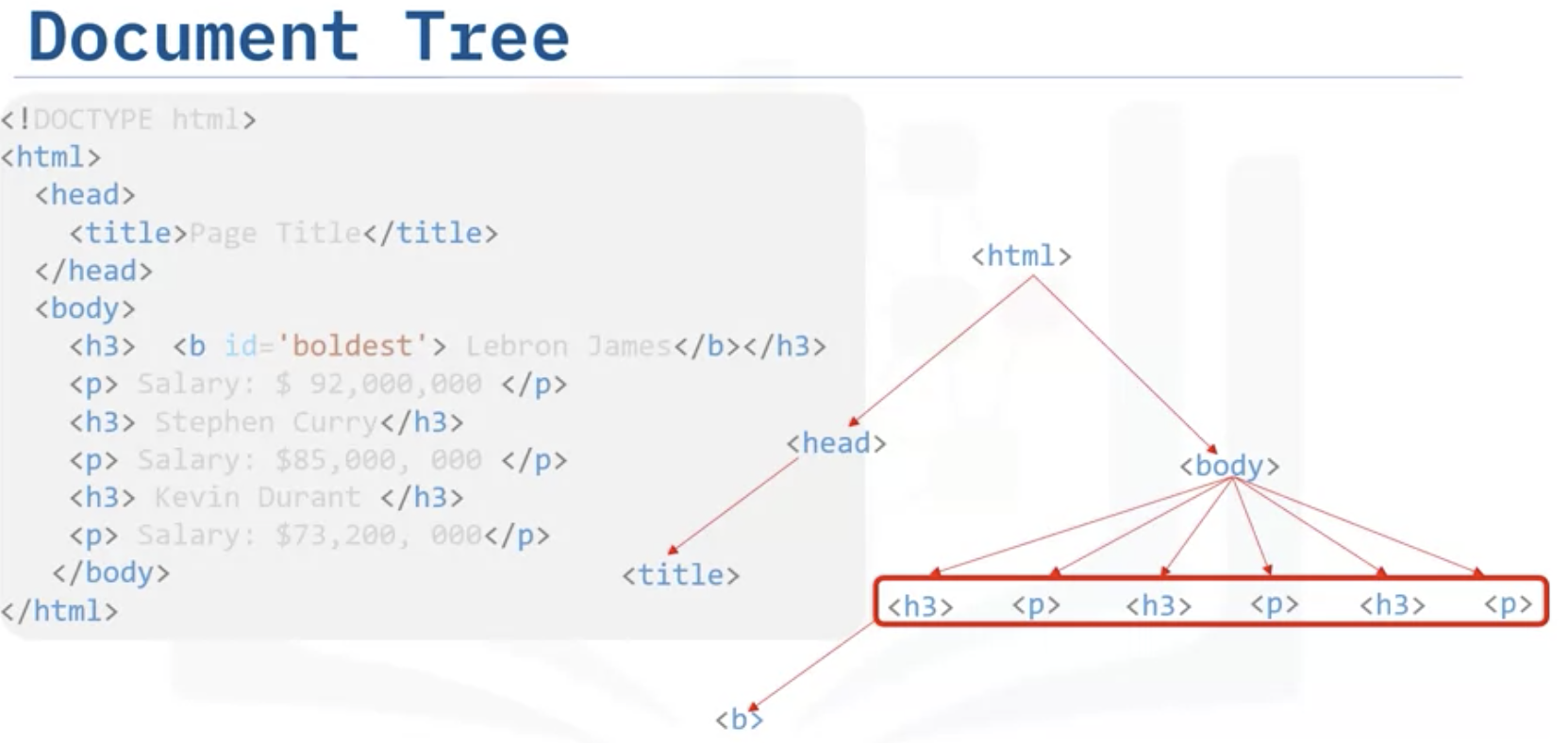
HTML Trees
: HTML tag is parents of below tags. head and body are in the same level (siblings) and the others are child tags of them.
HTML Tables
<table>
<tr>
<td> ,,,</td>
</tr>
</table>
Webscraping
: automatically extract information from a website and can easily be accomplished within a matter of minutes.
: We need python code + 2 modules (requests and beautiful soaps)
1) import beautifulSoup
: is a python library for pulling data out of HTML and XML files.
: Store the webpage HTML as a string in the variable HTML. To parse a document, pass it into the BeautifulSoup constructor.
-> then we get the beautifulSoup object (soup) which represents the document as a nested data structure

2)find_all
table_row = table.find__all(name='tr')
:loos through a tag's descendants and retrieves all descendants that match your filters.
:The methods signature for find_all(name, attrs, recursive, string, limit, **kwargs)
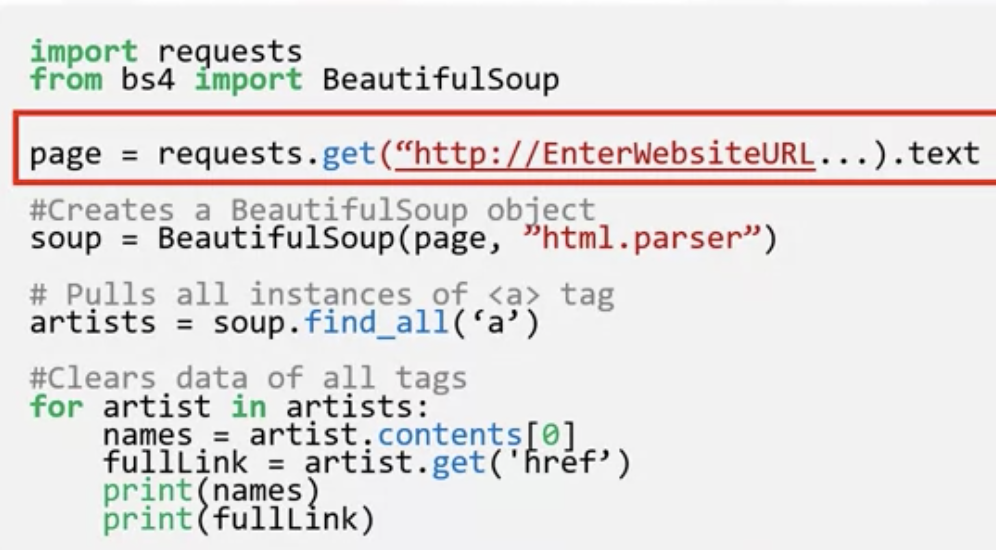
#HOW TO APPLY BeautifulSoup to a webpage.
1. import modules (requests, BeautifulSoup)
2. using get method to download the webpage
3. beautifulSoup object creating
Exercise
!pip install bs4 #!pip install requests
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup # this module helps in web scrapping.
import requests # this module helps us to download a web page%%html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>Page Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<h3><b id='boldest'>Lebron James</b></h3>
<p> Salary: $ 92,000,000 </p>
<h3> Stephen Curry</h3>
<p> Salary: $85,000, 000 </p>
<h3> Kevin Durant </h3>
<p> Salary: $73,200, 000</p>
</body>
</html>#We can store it as a string in the variable HTML.
html="<!DOCTYPE html><html><head><title>Page Title</title></head><body><h3><b id='boldest'>Lebron James</b></h3><p> Salary: $ 92,000,000 </p><h3> Stephen Curry</h3><p> Salary: $85,000, 000 </p><h3> Kevin Durant </h3><p> Salary: $73,200, 000</p></body></html>"
#To parse a document, pass it into the BeautifulSoup constructor, the BeautifulSoup object,
#which represents the document as a nested data structure:
soup = BeautifulSoup(html, 'html5lib')
#We can use the method prettify() to display the HTML in the nested structure:
print(soup.prettify())1. convert to Unicode (similar to ASCII)
2. HTML entities are converted to Unicode
3. Beautiful Soup transforms a complex HTML document into a complex tree of Python Objects.
(Beautiful Soup object can create other types of objects)
#we can get the designated data we want using Tag
tag_object=soup.title
print("tag object:",tag_object)
print("tag object type:",type(tag_object))
#if there are more than 1 tag, first one will be called
tag_object=soup.h3
tag_object
#We can access to its parent or sibling
parent_tag=tag_child.parent
parent_tag
sibling_1=tag_object.next_sibling
sibling_1HTML Attributes
If the tag has attributes, the tag id="boldest" has an attribute id whose value is boldest. You can access a tag’s attributes by treating the tag like a dictionary:
[22]: tag_child['id']
[22]: 'boldest'
You can access that dictionary directly as attrs:
[23]: tag_child.attrs
[23]: {'id': 'boldest'}
You can also work with Multi-valued attribute check out [1] for more.
We can also obtain the content if the attribute of the tag using the Python get() method.
[24]: tag_child.get('id')
[24]: 'boldest'
https://gist.github.com/ca23b851f884f278a834b3d24309db2a
Created on Skills Network Labs
Created on Skills Network Labs. GitHub Gist: instantly share code, notes, and snippets.
gist.github.com