2021. 5. 7. 20:18ㆍData science/Database
1. Working with csv files ; comma or semi-colon separated values
2. Querying column names with mixed case (upper and lower) - when it's mixed "Id", use double quotes
3. spaces and special characters - database may change space to underscore( _ ) and these should be within the double quotes
4. in Jupyter notebooks

5. Splitting queries to multiple lines in Jupyter: use \
%sql select "Id", "Name_of_Dog", \
from dogs \
where "Name_of_Dog" ='Hungry'%%sql
select "Id", "Name_of_Dog",
from dogs
where "Name_of_Dog" ='Hungry'
6. Restricting the # of rows retrieved - LIMIT clause (select * from census_data LIMIT 3)
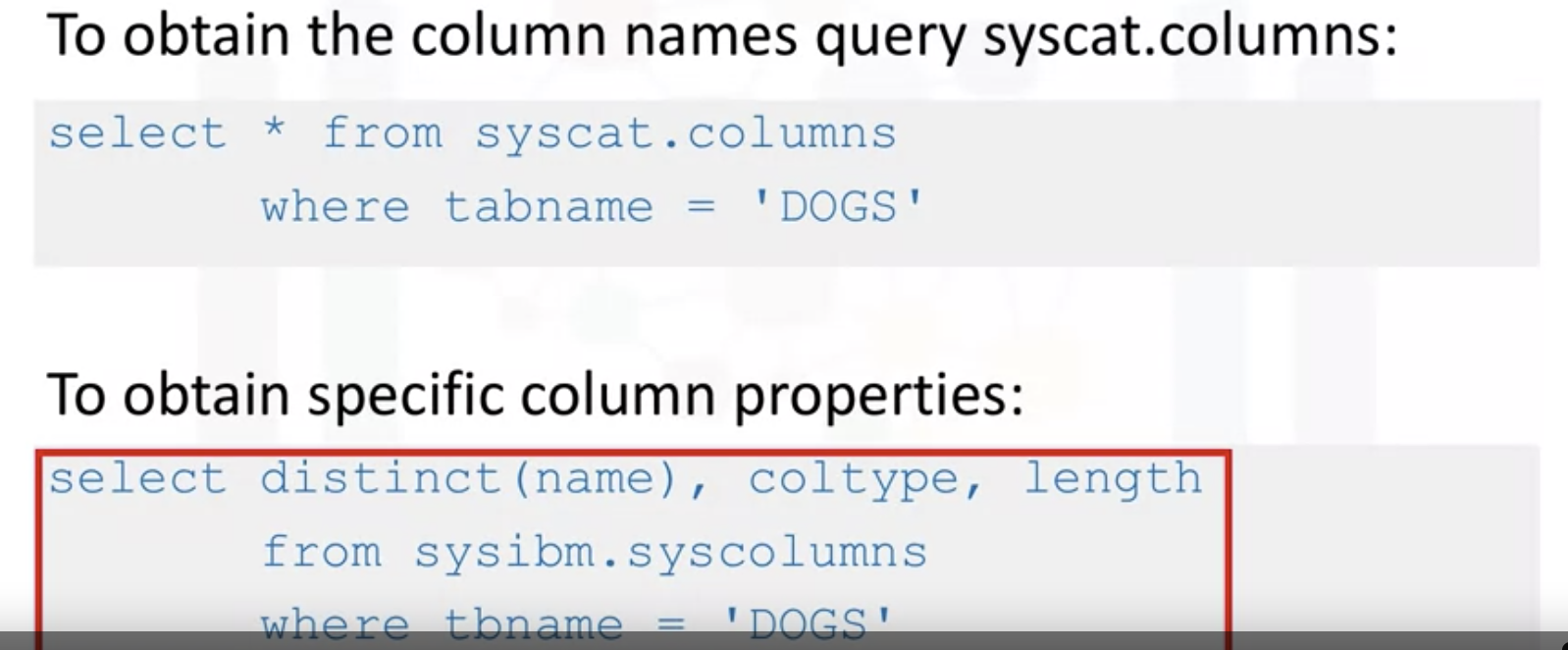
7. Getting a list of tables in the database: If you don't know the name of the tables
: DB2 - SYSCAT.TABLES / SQL Server - INFORMATION_SCHEMA.TABLES / Oracle - ALL_TABLES or USER_TABLES
select TABSCHEMA, TABNAME, CREATE_TIME
from syscat.tables
where tabschema = 'ABC12345'8.Getting table properties : select * from syscat.tables
* to check the last version
select TABSCHEMA, TABNAME, CREATE_TIME
from syscat.tables
where tabschema='LCT12330'
9. Getting a list of columns in the database